The abstract XML Schema components, as described in
XML Schema Part 1: Structures
of the Standard, are related according to the following
hierarchy:
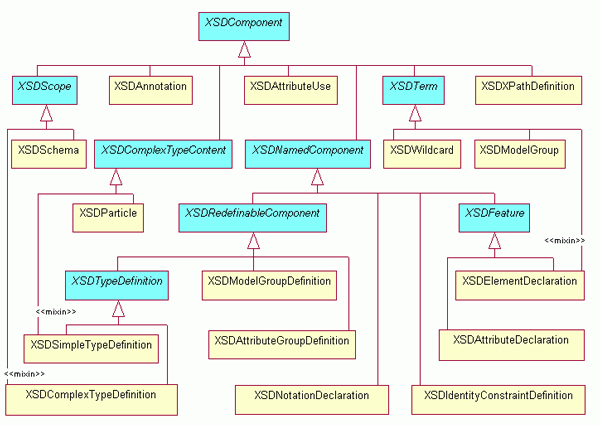
The figure above displays the hierarchy of the XML
Schema Infoset model. The classes in light blue
represent abstract classes, whereas the classes in
light orange represent the concrete classes.
Here is a short description of some of the classes that
you will need to understand:
-
XSDComponent: is the base class for all of the
XML Schema Infoset model classes.
-
XSDSchema: is the concrete class representing
the xml schema root object (<xsd:schema
...>)
-
XSDAnnotation: is the concrete class
representing xml schema components annotations
(<xsd:annotation>)
-
XSDSimpleTypeDefinition: is the concrete class
representing a simple type (<xsd:simpleType ...>)
-
XSDComplexTypeDefinition: is the concrete class
representing a complex type (<xsd:complexType ...>)
-
XSDElementDeclaration: is the concrete class
representing an element; either global, local or
reference (<xsd:element ...>)
-
XSDAttributeDeclaration: is the concrete class
representing an attribute; either global,local
or reference (<xsd:attribute ...>)
-
XSDAttributeGroupDefinition: is the concrete
class representing an attribute group (<xsd:attributeGroup ...>)
-
XSDModelGroupDefinition: is the concrete class
representing a group; either global or reference
(<xsd:group ...>)
-
XSDModelGroup: is the concrete class
representing a local group (<xsd:sequence>, <xsd:choice>or
<xsd:all>)
-
XSDWildCard: is the concrete class representing
a wild card element or attribute (<xsd:any> or <xsd:anyAttribute>)